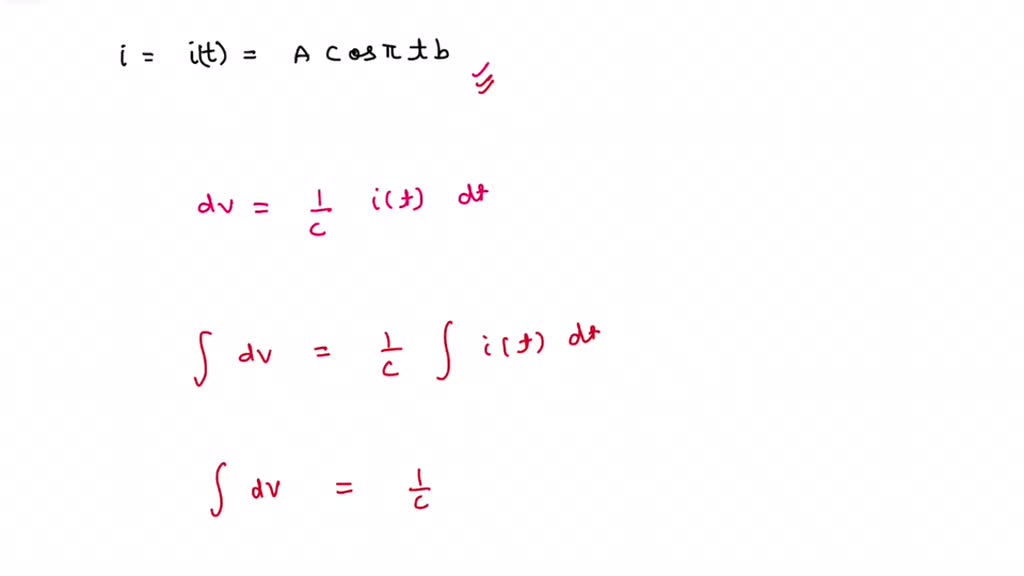Capacitor Equation I = C Dv/Dt . iv for a capacitor. Hence q = cv, and the current i is the rate of charge on the. ohm’s law for capacitor: But current is charge flow, or dq/dt. $i = \text c \,\dfrac{dv}{dt}$ $\text c$ is the capacitance, a physical property of the capacitor. We generally don’t work in q, we like i and v. Where i is the instantaneous current. So if q = cv, and i=dq/dt. Q = cv by differentiating the equation, we get: Electrical engineering > unit 2. i=c*dv/dt this equation relates the current to the voltage what this. C is the capacitance of the capacitor. the quantity c =áe/d is the capacitance and is measured in farads (f).
from www.numerade.com
Electrical engineering > unit 2. ohm’s law for capacitor: Where i is the instantaneous current. C is the capacitance of the capacitor. iv for a capacitor. $i = \text c \,\dfrac{dv}{dt}$ $\text c$ is the capacitance, a physical property of the capacitor. Hence q = cv, and the current i is the rate of charge on the. We generally don’t work in q, we like i and v. Q = cv by differentiating the equation, we get: But current is charge flow, or dq/dt.
SOLVED A fundamental relationship for a capacitor is the relationship
Capacitor Equation I = C Dv/Dt So if q = cv, and i=dq/dt. Hence q = cv, and the current i is the rate of charge on the. C is the capacitance of the capacitor. So if q = cv, and i=dq/dt. $i = \text c \,\dfrac{dv}{dt}$ $\text c$ is the capacitance, a physical property of the capacitor. i=c*dv/dt this equation relates the current to the voltage what this. We generally don’t work in q, we like i and v. iv for a capacitor. But current is charge flow, or dq/dt. Q = cv by differentiating the equation, we get: ohm’s law for capacitor: Electrical engineering > unit 2. Where i is the instantaneous current. the quantity c =áe/d is the capacitance and is measured in farads (f).
From www.protoexpress.com
Basic Electronic Components Sierra Circuits Capacitor Equation I = C Dv/Dt Where i is the instantaneous current. ohm’s law for capacitor: i=c*dv/dt this equation relates the current to the voltage what this. So if q = cv, and i=dq/dt. iv for a capacitor. But current is charge flow, or dq/dt. $i = \text c \,\dfrac{dv}{dt}$ $\text c$ is the capacitance, a physical property of the capacitor. We. Capacitor Equation I = C Dv/Dt.
From www.youtube.com
Derive the Capacitor Charging Equation (Using 1st Order Differential Capacitor Equation I = C Dv/Dt So if q = cv, and i=dq/dt. ohm’s law for capacitor: Electrical engineering > unit 2. i=c*dv/dt this equation relates the current to the voltage what this. But current is charge flow, or dq/dt. iv for a capacitor. the quantity c =áe/d is the capacitance and is measured in farads (f). Q = cv by differentiating. Capacitor Equation I = C Dv/Dt.
From www.numerade.com
SOLVED (a) In the circuit given bellow determine an expression for the Capacitor Equation I = C Dv/Dt the quantity c =áe/d is the capacitance and is measured in farads (f). So if q = cv, and i=dq/dt. Q = cv by differentiating the equation, we get: Hence q = cv, and the current i is the rate of charge on the. i=c*dv/dt this equation relates the current to the voltage what this. We generally don’t. Capacitor Equation I = C Dv/Dt.
From www.youtube.com
Capacitor Current Equation i=c*dv/dt YouTube Capacitor Equation I = C Dv/Dt iv for a capacitor. So if q = cv, and i=dq/dt. Q = cv by differentiating the equation, we get: $i = \text c \,\dfrac{dv}{dt}$ $\text c$ is the capacitance, a physical property of the capacitor. the quantity c =áe/d is the capacitance and is measured in farads (f). C is the capacitance of the capacitor. But. Capacitor Equation I = C Dv/Dt.
From www.numerade.com
SOLVED A circuit consists of a resistor of resistance R and a Capacitor Equation I = C Dv/Dt C is the capacitance of the capacitor. We generally don’t work in q, we like i and v. $i = \text c \,\dfrac{dv}{dt}$ $\text c$ is the capacitance, a physical property of the capacitor. So if q = cv, and i=dq/dt. iv for a capacitor. Where i is the instantaneous current. But current is charge flow, or dq/dt.. Capacitor Equation I = C Dv/Dt.
From www.slideserve.com
PPT Electricity & Circuits An introduction for neuroscientists Capacitor Equation I = C Dv/Dt But current is charge flow, or dq/dt. ohm’s law for capacitor: i=c*dv/dt this equation relates the current to the voltage what this. Where i is the instantaneous current. Electrical engineering > unit 2. Q = cv by differentiating the equation, we get: the quantity c =áe/d is the capacitance and is measured in farads (f). C is. Capacitor Equation I = C Dv/Dt.
From www.allaboutcircuits.com
Capacitors and Calculus Capacitors Electronics Textbook Capacitor Equation I = C Dv/Dt C is the capacitance of the capacitor. Electrical engineering > unit 2. So if q = cv, and i=dq/dt. But current is charge flow, or dq/dt. $i = \text c \,\dfrac{dv}{dt}$ $\text c$ is the capacitance, a physical property of the capacitor. We generally don’t work in q, we like i and v. iv for a capacitor. Q. Capacitor Equation I = C Dv/Dt.
From www.transtutors.com
(Get Answer) The CurrentVoltage Relationship Of A Capacitor Is I=C C Capacitor Equation I = C Dv/Dt iv for a capacitor. Where i is the instantaneous current. Electrical engineering > unit 2. ohm’s law for capacitor: i=c*dv/dt this equation relates the current to the voltage what this. C is the capacitance of the capacitor. We generally don’t work in q, we like i and v. $i = \text c \,\dfrac{dv}{dt}$ $\text c$ is. Capacitor Equation I = C Dv/Dt.
From electronica.guru
¿Cómo se mantiene constante la corriente en un capacitor ideal Capacitor Equation I = C Dv/Dt So if q = cv, and i=dq/dt. Where i is the instantaneous current. Hence q = cv, and the current i is the rate of charge on the. But current is charge flow, or dq/dt. the quantity c =áe/d is the capacitance and is measured in farads (f). i=c*dv/dt this equation relates the current to the voltage what. Capacitor Equation I = C Dv/Dt.
From www.chegg.com
Solved (a) Using the knowledge that i = C dv/dt, use Capacitor Equation I = C Dv/Dt So if q = cv, and i=dq/dt. the quantity c =áe/d is the capacitance and is measured in farads (f). But current is charge flow, or dq/dt. We generally don’t work in q, we like i and v. iv for a capacitor. $i = \text c \,\dfrac{dv}{dt}$ $\text c$ is the capacitance, a physical property of the. Capacitor Equation I = C Dv/Dt.
From engr44tnguyen.blogspot.com
Engineering 44 tnguyen DAY 13 Capacitors and Inductors/ Capacitor Capacitor Equation I = C Dv/Dt Electrical engineering > unit 2. i=c*dv/dt this equation relates the current to the voltage what this. Hence q = cv, and the current i is the rate of charge on the. ohm’s law for capacitor: C is the capacitance of the capacitor. So if q = cv, and i=dq/dt. We generally don’t work in q, we like i. Capacitor Equation I = C Dv/Dt.
From www.chegg.com
Solved I thought it was the formula i = C*dv/dt and then one Capacitor Equation I = C Dv/Dt $i = \text c \,\dfrac{dv}{dt}$ $\text c$ is the capacitance, a physical property of the capacitor. ohm’s law for capacitor: C is the capacitance of the capacitor. Where i is the instantaneous current. Hence q = cv, and the current i is the rate of charge on the. Electrical engineering > unit 2. Q = cv by differentiating. Capacitor Equation I = C Dv/Dt.
From dxonqlkxi.blob.core.windows.net
Capacitance Resistance Problems at Gary Reyes blog Capacitor Equation I = C Dv/Dt iv for a capacitor. i=c*dv/dt this equation relates the current to the voltage what this. $i = \text c \,\dfrac{dv}{dt}$ $\text c$ is the capacitance, a physical property of the capacitor. Q = cv by differentiating the equation, we get: ohm’s law for capacitor: C is the capacitance of the capacitor. So if q = cv,. Capacitor Equation I = C Dv/Dt.
From www.thestudentroom.co.uk
Voltage across Capacitor equation derivation. Pls help, much Capacitor Equation I = C Dv/Dt But current is charge flow, or dq/dt. $i = \text c \,\dfrac{dv}{dt}$ $\text c$ is the capacitance, a physical property of the capacitor. Hence q = cv, and the current i is the rate of charge on the. i=c*dv/dt this equation relates the current to the voltage what this. C is the capacitance of the capacitor. Where i. Capacitor Equation I = C Dv/Dt.
From www.numerade.com
SOLVED A fundamental relationship for a capacitor is the relationship Capacitor Equation I = C Dv/Dt We generally don’t work in q, we like i and v. ohm’s law for capacitor: But current is charge flow, or dq/dt. C is the capacitance of the capacitor. Q = cv by differentiating the equation, we get: So if q = cv, and i=dq/dt. iv for a capacitor. $i = \text c \,\dfrac{dv}{dt}$ $\text c$ is. Capacitor Equation I = C Dv/Dt.
From wiredatajestuno.z21.web.core.windows.net
Capacitor Charge And Discharge Circuit Capacitor Equation I = C Dv/Dt Q = cv by differentiating the equation, we get: $i = \text c \,\dfrac{dv}{dt}$ $\text c$ is the capacitance, a physical property of the capacitor. the quantity c =áe/d is the capacitance and is measured in farads (f). Electrical engineering > unit 2. Hence q = cv, and the current i is the rate of charge on the.. Capacitor Equation I = C Dv/Dt.
From slideplayer.com
ENGS2613 Intro Electrical Science Week ppt download Capacitor Equation I = C Dv/Dt Where i is the instantaneous current. Electrical engineering > unit 2. We generally don’t work in q, we like i and v. Q = cv by differentiating the equation, we get: the quantity c =áe/d is the capacitance and is measured in farads (f). But current is charge flow, or dq/dt. i=c*dv/dt this equation relates the current to. Capacitor Equation I = C Dv/Dt.
From www.allaboutcircuits.com
Capacitors and Calculus Capacitors Electronics Textbook Capacitor Equation I = C Dv/Dt Hence q = cv, and the current i is the rate of charge on the. $i = \text c \,\dfrac{dv}{dt}$ $\text c$ is the capacitance, a physical property of the capacitor. C is the capacitance of the capacitor. We generally don’t work in q, we like i and v. So if q = cv, and i=dq/dt. Electrical engineering >. Capacitor Equation I = C Dv/Dt.